What is Look-Up Tables (LUTs) in FPGA (Look-Up Tables, LUT là gì?)
In this article we explore two questions:
- Location of LUT in an FPGA
- The role of LUT in an FPGA
1./ What is Look-Up Table (LUT)? Look-Up Table là gì?
+ What is Look-Up Tables (LUT): LUT or Look-Up Table, is a table that determines output values for combinations of input values, it can be thought of similarly to the truth table of digital circuits. K-input LUT (k-LUT, LUTk) is used to describe a LUT with k-input.
+ LUT classification: LUTs are classified based on the number of inputs to the LUT.
Example: two-input LUT (LUT2), three-input LUT (LUT3), four-input LUT (LUT4), five-input LUT (LUT5), six-input LUT (LUT6).
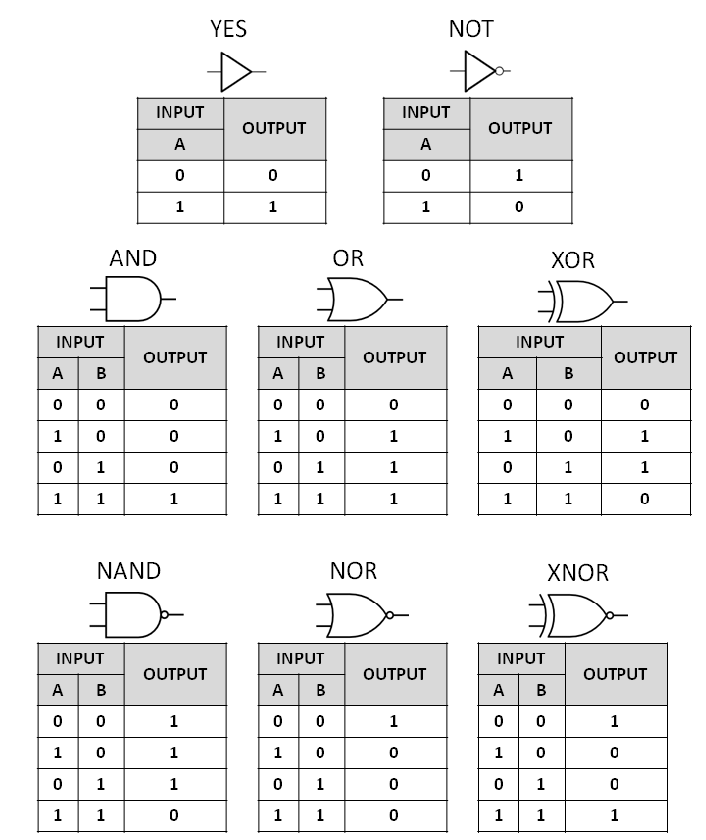
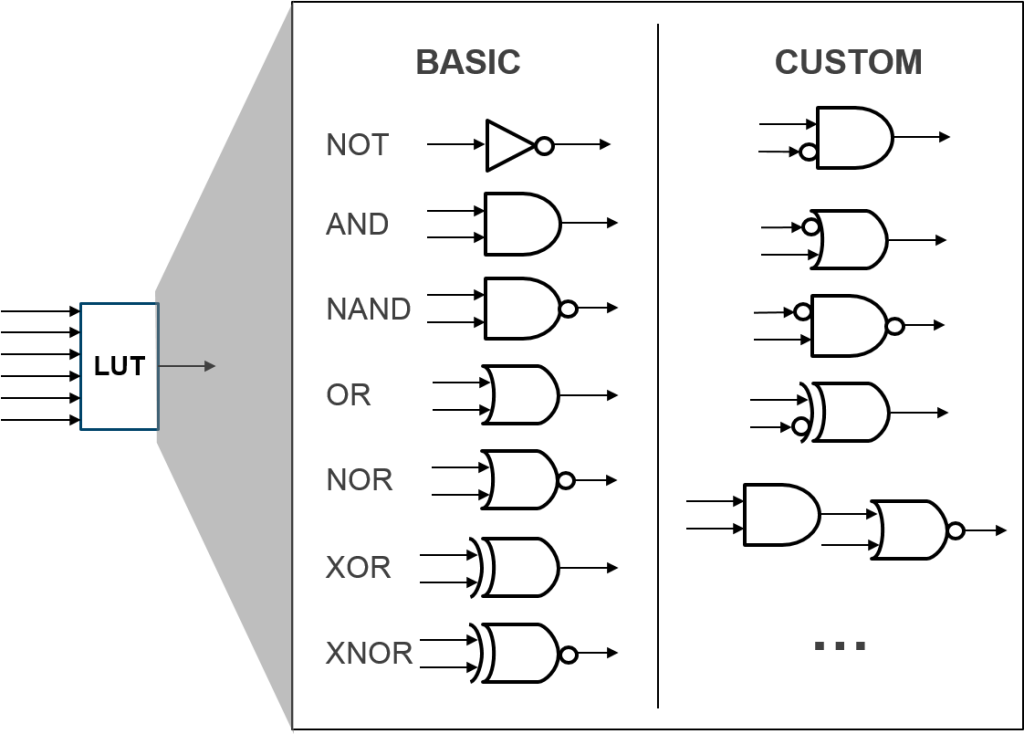
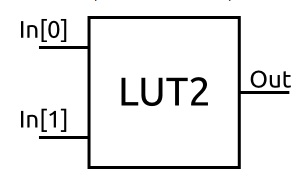
We see the truth table of basic gate logic, and how a LUT2 describes those basic gate logic. And the truth table of logic gates is the same as the truth table of that logic gate when described by LUT2.
2./ Location of LUT in an FPGA
An FPGA circuit consists of many configurable logic blocks called CLBs (Configuarable Logic Block).
=> Each CLB contains a number of logic elements called Logic Cells (LC).
==> Each LC includes binary inputs, and programmable outputs.
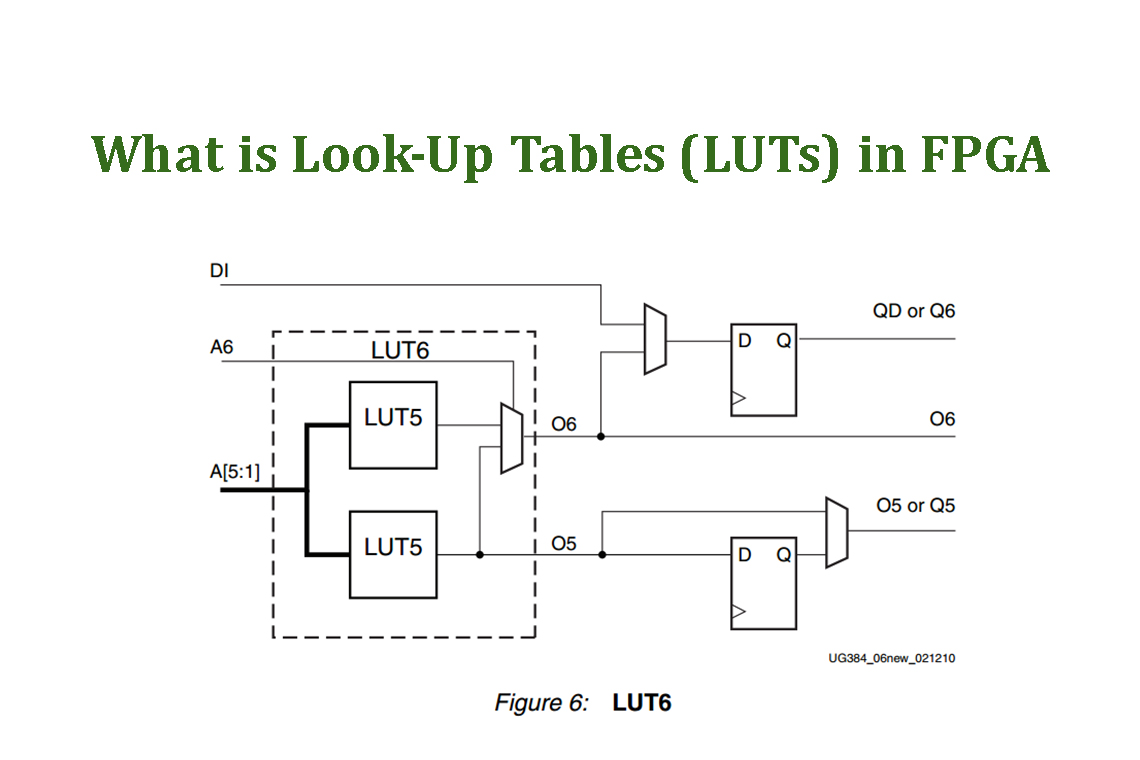
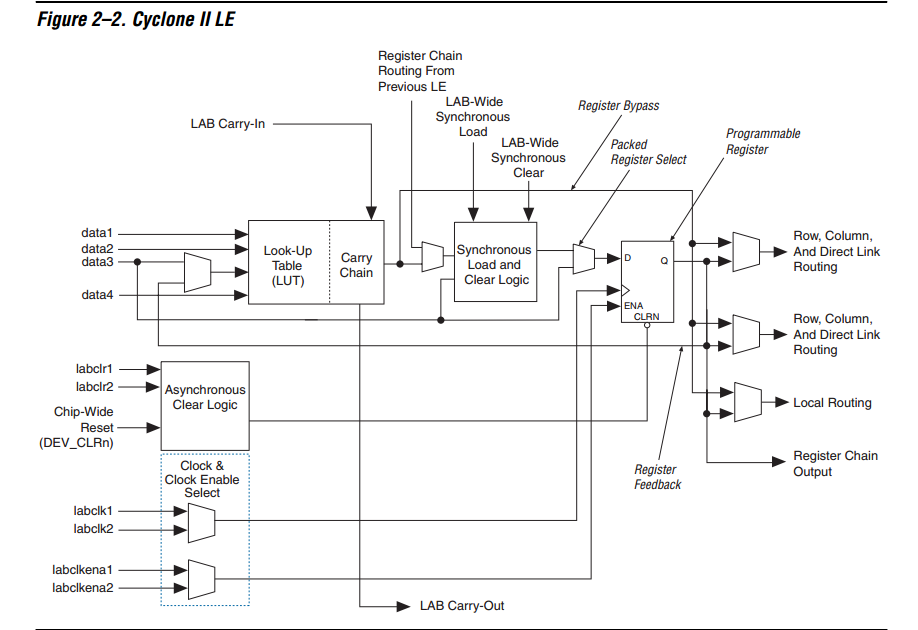
===> Inside each LC contains a logic function generator. The logic function generator can be implemented using a LUT (Look-Up Table memory) or a combination of mutiplexers and gates.
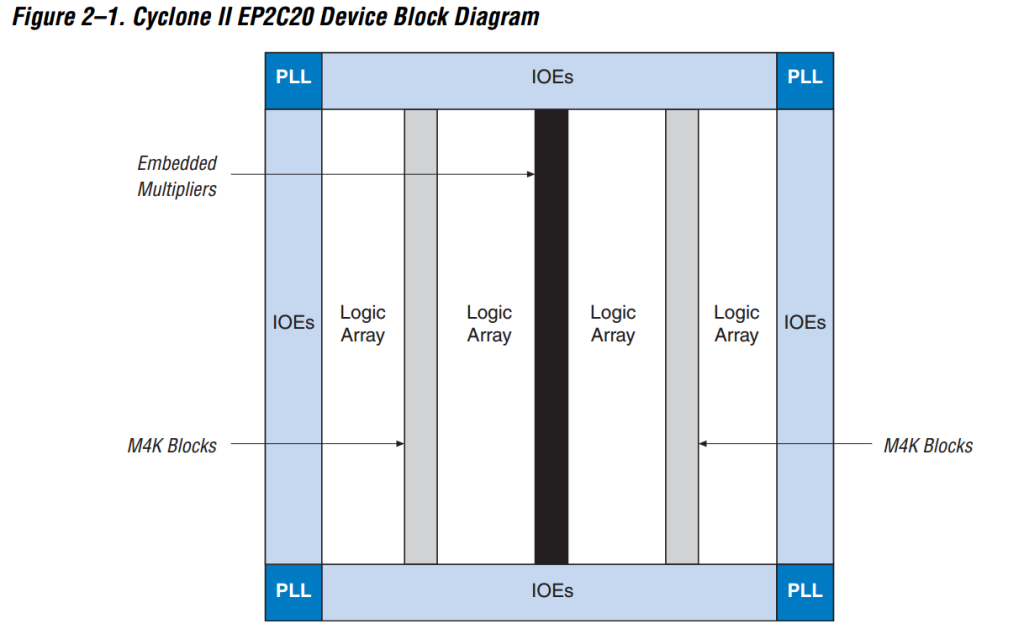
Example with Cyclone II Altera FPGA:
Altera FPGA with Logic Array Blocks (LABs),
=> Each LAB will include Logic Elements (LEs).
==> Each LE will include LUT4s (four-input look-up tables)
Example with Virtex-6, Spartan-6 and 7 series XILINX FPGA:
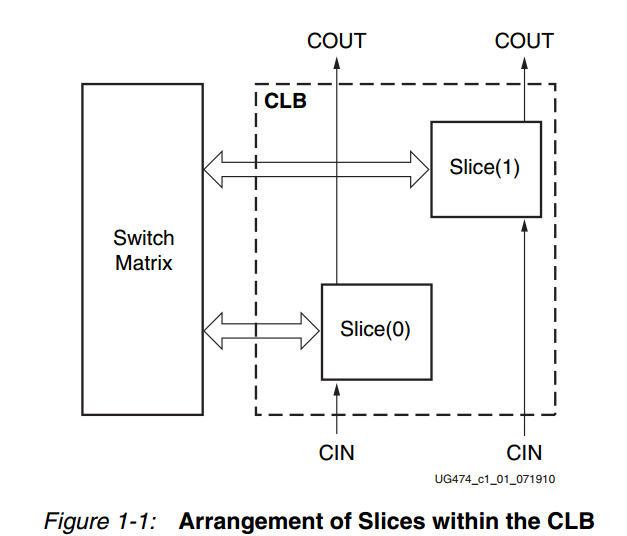
XILINX FPGA with CLBs (Configuarable Logic Blocks)
=> Each CLB include a pair of Slices
==> Each Slice will include two Logic Cells (LCs)
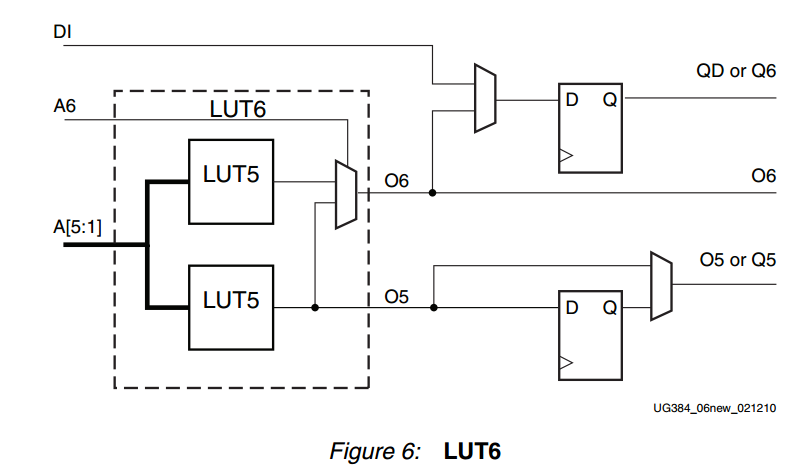
===> Each LC include one LUT6 (6-input look-up table)
3./ The role of LUT in an FPGA
+ Do you also have the same question as me: when I learn about Digital System, I learn about AND, OR, NOT Gate,…, Boolean algebra logic, but when I learn about structure of FPGA, I don’t see anything, I never saw the appearance of these gates in the structure of the FPGA. I was also confused by this.
Does the FPGA have anything to do with what I have learned about Digital System?
+ LUT is an FPGA solution to implement logic functions. You can also use LUT to create AND, OR, NOT, … gates.
Instead of connecting logic gates, you describe a digital circuit with the input and output logic values of that digital circuit in look-up tables (LUT).
This is similar to creating a truth table for logic gates, or logic functions, or digital circuits.
Creating look-up tables will be easier to understand, easier to implement, and more convenient in storing information than connecting circuit lines for logic gates and logic blocks.
+ LUT is an important component in FPGA.
+ Advantages of LUT: Flexibility allowing the implementation of many complex logic functions and many types of digital circuits.
+ Disadvantages of LUT: there is a limitation in the number of inputs and outputs, it creates propagation delay due to the need for memory access time to look up the output value of the LUTs.

List of FPGA Tutorials

The AND gate
Có thể bạn cũng thích

How to Install ModelSim – Intel FPGA Starter Edition on Ubuntu 22.04
Tháng 6 14, 2025
Trứng chiên lá mơ
Tháng 5 25, 2025
